
3D Laser Scanning is one of the most innovative technologies enabling fast capturing of three-dimensional measurement data. The result of its use is a data base including information on millions of points, which was impossible to achieve with the traditional methods used so far.
The laser beam reaches the scanned object point by point, and returns to the scanner with the information on their position in space. This method makes it possible to measure objects regardless of their shape and complexity. The information obtained this way is called a point cloud, meaning a data base of points and their coordinates (X, Y, Z) as well as additional information such as the color.
The point cloud is very accurate, and can be used itself or processed further to achieve as-built documentation such as 3D CAD models, 2D drawings and many more.
- huge amount of 3D data
- much shorter measurement time
- non-invasive (non-touch) measurement, providing increased safety
- around measured objects
- all data is 100% digital
- easy use of data (it can be saved in a text file - multi-purpose)
- convenient visual presentation of data
- more manageability of various limitations (e.g. scaffolding)
- thanks to distant measurements
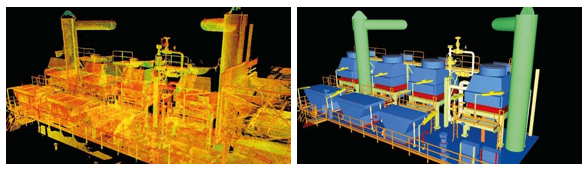
Applications
Many different technologies can be used to build 3D-scanning devices; each technology comes with its own limitations, advantages and costs.
In principle, the Scanners we operate works by sending an infrared laser beam into the center of its rotating mirror. The mirror deflects the laser beam on a vertical rotation around the environment being scanned; scattered light from surrounding objects is then reflected back into the scanner.
The scanners operate with extremely high accuracy +/- 0.5 mm in range up to 300 meter. Provides high (HD) photorealistic 3D color scans from build in color camera, including compass and altimeter for optimal scan orientation and level positioning.
Our scanning and engineering process are as follows:
- Laser scanning
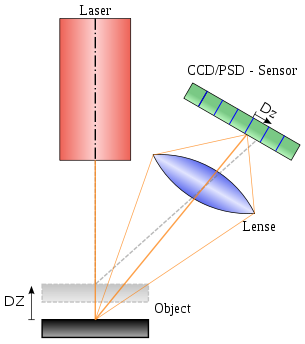
- Registration
- Point clouds
- 3D modelling (Primitive modeller)
- Intelligent models (Intelligente - PDMS)
- Panorama pictures
- Scan Data Management
- Web portals
- Clash detection
- Visualization
- Electronic measurements
- Master Grid
- Prefab control
